Golfer’s elbow
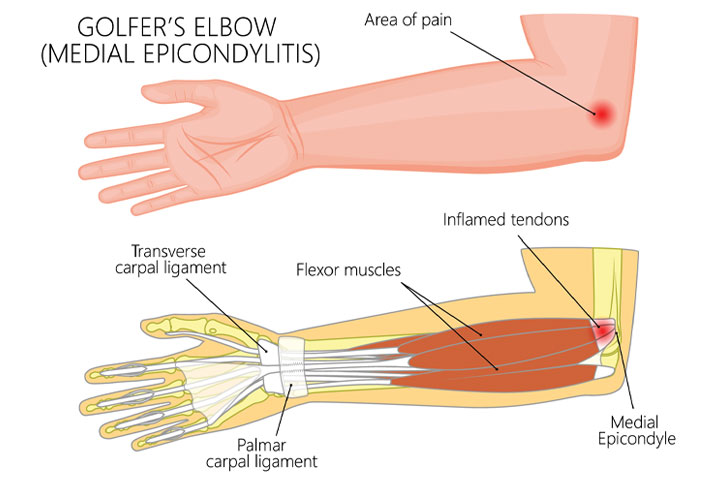
Golfer’s elbow is a condition characterised by pain on the inner aspect of the elbow.
The Flexor muscles of the forearm attach to the medial epicondyle of the humerus bone through a Common flexor origin. Whenever, they are subjected to trauma or Overuse injury, there can be inflammation of the common origin leading to Medial epicondylitis.
The prevalence of Golfer’s elbow in general population is estimated to be <1%.
Golfer’s elbow is a misnomer as it is also seen in people from other professions involving overuse of the Flexors of forearm like plumbers, carpenters, painters, IT professionals.
Signs and Symptoms
- Stabbing type of pain on the inner aspect of elbow which can radiate to the forearm
- Aggravation of pain on activities like shaking hands, gripping an object or holding a coffee mug.
- Stiffness in the elbow or weakness in the hands
- Numbness or tingling usually in the little and ring fingers.
Risk Factors
- Age. While tennis elbow affects people of all ages, it's most common in adults between the ages of 30 and 50.
- Occupation. People who have jobs that involve repetitive motions of the wrist and arm are more likely to develop Golfer’s elbow. Examples include plumbers, painters, carpenters, butchers and cooks
- Certain sports.Participating in throwing sports with improper pitching technique. Football, archery and javelin throwing also can cause golfer's elbow.
JEEVISHA protocol for management of Golfer’s elbow
- Conservative management: Lifestyle modification with avoiding of activities which are the main culprits play a very important role in its management. Use of elbow splints/braces to reduce excessive stress on the muscles also proves very helpful. Icing is also generally advised 2-3 times a day to reduce the inflammation.
- Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy plays a very important role in fighting this painful condition. With a team of dedicated physiotherapist, patient is further evaluated and accordingly a plan is prepared for first reducing pain with different modalities and then slowly rehabilitating elbow for normal functioning.
- Medications: In the initial course of the management of this condition, patients may be prescribed some Anti-inflammatory medications. Some other medications may be prescribed depending on the condition of the patient, which is individualized from patient to patient basis.
Targeted treatment
- Ultrasound guided injection
- Ultrasound guided Dextrose prolotherapy
- Ultrasound guided Platelet rich plasma Prolotherapy